How to Choose the Right Electronic Valve for Your Application?
Choosing the right electronic valve for your application is critical. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned expert in fluid dynamics, "The heart of any system lies within its valves." This statement highlights the importance of selecting the appropriate electronic valve to optimize performance.
Factors like flow rate, pressure, and material compatibility play a significant role. Many users overlook these details. They may choose a valve based on immediate availability rather than suitability. This can lead to inefficiencies or even system failures.
A reliable electronic valve can enhance operational efficiency. It can reduce maintenance costs and improve longevity. Yet, not all valves are created equal. It’s essential to assess your specific needs before making a decision. Remember, complexity is not always the answer. Sometimes, the simplest solution is the best.

Understanding the Basics of Electronic Valves and Their Applications
Electronic valves play a critical role in many systems. They control fluid flow in various applications, from industrial machinery to home automation. Understanding their basics can help you make informed decisions.
Choose the right type based on your needs. Normally, you’ll encounter solenoid valves, pneumatic valves, and proportional valves. Each serves different functions. For instance, a solenoid valve operates quickly. It’s ideal for applications needing rapid response. Think about the environment too. Some valves are not suited for extreme temperatures or pressures.
**Tips:** Consider your system's requirements. Are you controlling gases or liquids? What is the required flow rate? Also, assess the power source available. This may limit your choices.
Pay attention to specifications. Not all valves are equal. What seems perfect may fail in your application. Research and assess options thoroughly. Check for compatibility with your existing setup. Sometimes it’s beneficial to consult with a professional.
**Tips:** Always have a backup plan. Choose valves with spare parts available. When in doubt, prioritize reliability over cost. Balancing performance and budget can be tricky but essential for success.
How to Choose the Right Electronic Valve for Your Application?
| Application | Valve Type | Operating Voltage | Flow Rate (L/min) | Pressure Rating (bar) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Control | Solenoid Valve | 24V DC | 15 | 6 |
| Air Control | Pneumatic Valve | 110V AC | 30 | 8 |
| Chemical Processing | Electromagnetic Valve | 12V DC | 10 | 10 |
| HVAC Systems | On/Off Valve | 24V AC | 20 | 5 |
| Food Industry | Stainless Steel Valve | 220V AC | 25 | 7 |
Identifying Key Factors in Selecting an Electronic Valve
When selecting an electronic valve, various key factors must be considered. The operating environment impacts performance. For instance, high temperatures can affect valve functionality, leading to failures. In industries like chemical processing, 80% of valve failures are traced back to environmental conditions. Always check the temperature and pressure ratings.
Additionally, the medium being controlled plays a critical role. Will it handle corrosive fluids? Flow rates vary significantly across applications. A recent industry report highlighted that up to 40% of valve malfunctions stem from improper sizing. Size matters; a valve too small restricts flow, while one too large may lead to inefficiencies.
Control type is also essential. Will you use on-off or modulating control? Demand for precision is growing. Recent studies indicate that 35% of plant operators wish for more accuracy in valve operation. Reflect on how often adjustments will be needed. Inconsistent control can lead to energy waste. Electronic valves can enhance performance, but only when selected thoughtfully.
Types of Electronic Valves and Their Specific Uses
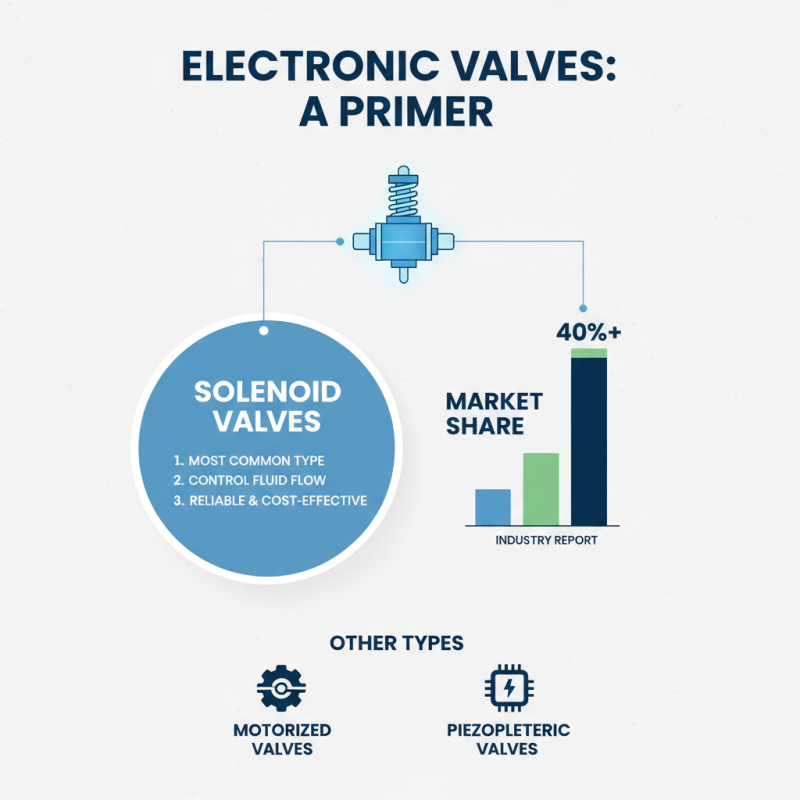
When selecting an electronic valve, understanding the types available is crucial. There are several categories of electronic valves. Each serves different applications. Solenoid valves are among the most common. They control the flow of fluids in various systems. According to a recent industry report, solenoid valves account for over 40% of the market due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Another popular type is the proportional valve. This valve type allows more precise control of flow rates. It is typically used in applications requiring detailed adjustments. They are often found in automated systems. An estimated 25% of industry professionals prefer proportional valves for their efficiency and accuracy.
Then, there are motorized valves. These valves integrate with electric motors for opening and closing. Industries involving large flow rates may find these most suitable. However, one notable drawback can be their complexity. Installation and troubleshooting may require specialized skills. Many professionals express concerns over maintenance. Ensuring the right valve type is essential to avoid costly mistakes down the line. The variances in usage highlight the importance of research and reflection before making a choice.
Evaluating Performance Specifications for Your Application Needs
When evaluating performance specifications for electronic valves, it's crucial to consider flow rates. Different applications require specific flow ranges. For instance, data shows that in chemical processing, valves designed for high flow rates can improve efficiency by up to 30%. Understanding the flow characteristics helps in choosing the right valve.
Pressure ratings also play a vital role. The pressure range can determine the longevity and reliability of a valve. Reports indicate that operating a valve near its maximum pressure can reduce its lifespan by 40%. Users must ensure that the selected valve can handle the expected pressure without compromising safety.
Temperature tolerance is another critical factor. Many processes involve extreme heat or cold. Choosing a valve with inadequate temperature ratings can lead to failures. It's essential to match the temperature specifications with the application's requirements. Systematic testing can reveal potential weaknesses early on. Finally, regular performance evaluations can help catch issues before they escalate.
Considering Cost, Maintenance, and Long-Term Reliability Factors
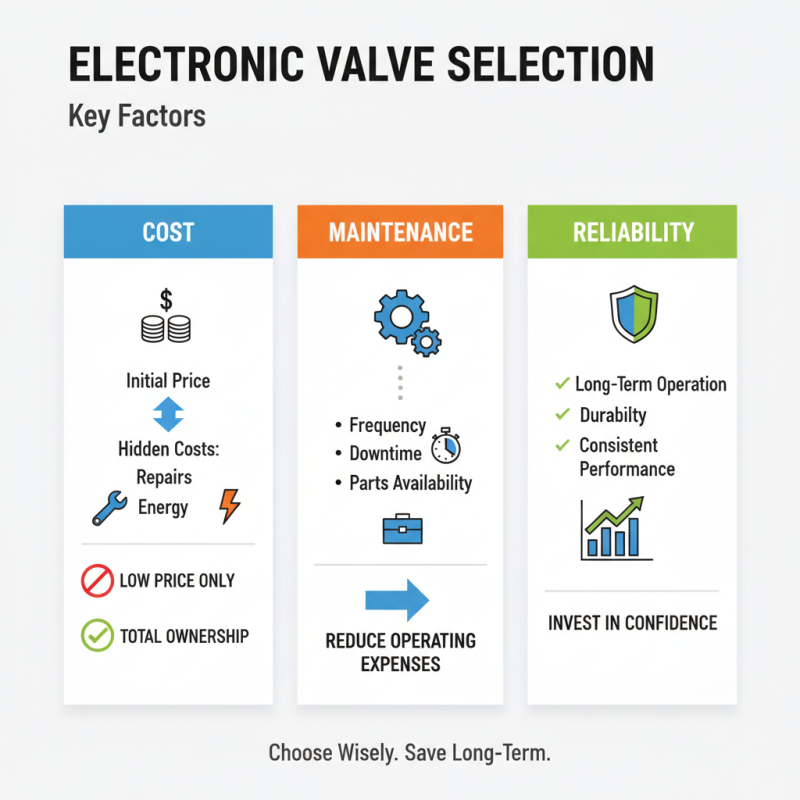
Choosing the right electronic valve requires careful consideration of various factors. Among these, cost, maintenance, and long-term reliability play crucial roles. A low-cost valve may seem appealing at first. However, hidden costs can emerge over time. Frequent repairs can quickly add up, outweighing initial savings.
Maintenance is another important aspect. Some valves may require regular calibration or component replacements. This can lead to unexpected downtime. To mitigate risks, opt for valves that are known for their durability. These choices can reduce the need for frequent maintenance. Identify models with simpler designs too. Fewer components often mean fewer potential failure points.
Long-term reliability is paramount. A valve that functions well today may not last years down the line. Researching warranty options can provide insight into expected lifespan. Look for testimonials or case studies related to specific applications. Such resources can highlight real-world performance. Ignoring these details may lead to regrets later on.
Related Posts
-

What is an Electronic Valve and How Does it Work in Modern Systems
-
How to Choose the Right Electronic Valve for Your System?
-
2026 Top Pressure Release Valve Features You Should Know?
-
How to Choose the Right Control Valve for Your Industrial Applications
-
Unlocking the Science Behind Cryogenic Valves: Essential Insights for Safe Operation
-

What is a Pressure Control Valve and How Does It Work in Different Applications
