2026 How to Choose the Right Solenoid Valve for Your Application?
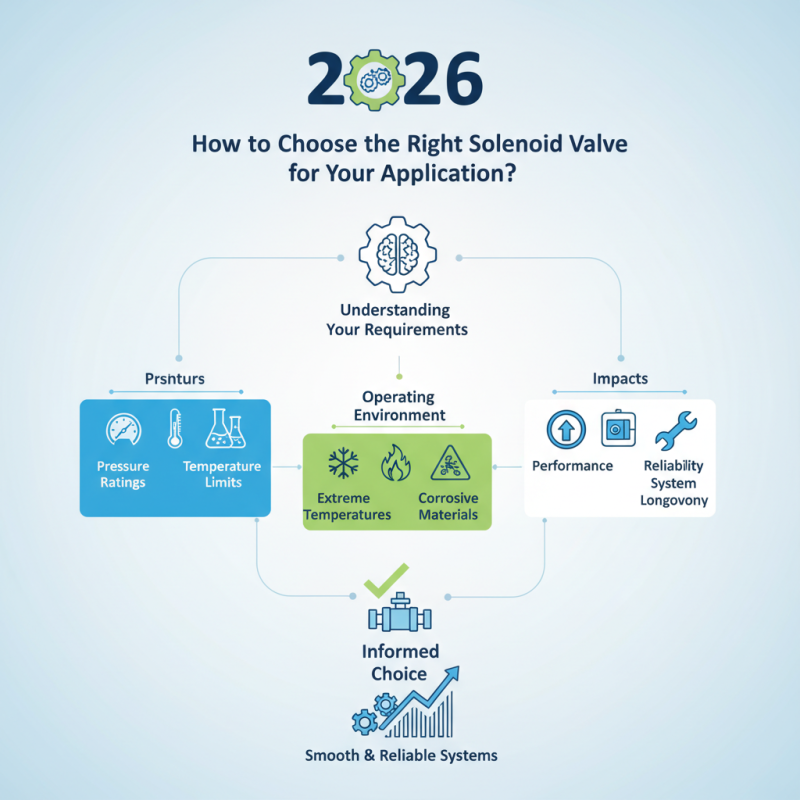
Choosing the right solenoid valve for your application can be a daunting task. Experts like John Smith, a leading figure in the solenoid valve industry, emphasize, “Understanding your requirements is crucial.” With numerous options available, it can be overwhelming to select the best valve.
Solenoid valves are essential components in many systems. They control fluid flow and pressure with precision. Selecting the wrong valve can lead to inefficient operations or even system failures. You need to consider various factors, such as pressure ratings, temperature limits, and fluid compatibility.
It's also important to reflect on the specific environment where the solenoid valve will operate. Will it face extreme temperatures or corrosive materials? These elements can significantly affect performance and longevity. Making an informed choice is vital to ensure your systems run smoothly and reliably.
Understanding Solenoid Valve Basics and Their Functions
Understanding solenoid valves is crucial for selecting the right one for any application. These devices control fluid flow through electromagnetic actions. A solenoid valve consists of a coil, armature, and a valve body. When electricity flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field. This movement opens or closes the flow path, enabling or stopping the fluid.
When choosing a solenoid valve, consider the medium it will control. Different fluids require specific materials to avoid corrosion. The valve's pressure rating also matters. High-pressure applications need robust designs. Not assessing the operating environment can lead to failures. For example, extreme temperatures can affect performance. This reality requires awareness and adaptability in your choice.
The valve's form factor is another key aspect. Depending on available space, size could limit options. Sometimes, an ideal valve may not fit due to spatial constraints. It’s essential to evaluate each aspect carefully. Making impulsive decisions can introduce inefficiencies. Understanding these fundamentals can significantly impact the overall system performance.
Key Specifications to Consider When Selecting a Solenoid Valve
When selecting a solenoid valve, several key specifications demand attention. First, consider the valve size. It must fit within your system without causing unnecessary pressure drops. A valve too large or too small can lead to malfunctions. Next, look at the voltage rating. Ensure it matches your power source. A mismatch can result in damage.
Another critical specification is the fluid type. Different solenoid valves handle various fluids, from water to oil. Ensure compatibility to avoid leaks or performance issues. You should also factor in the temperature range. Exceeding recommended limits can shorten the valve's lifespan. Lastly, examine the response time. A slow response may not suit applications requiring quick actuation.
It’s worth noting that the installation process affects performance. Improper installation can cause issues later. Testing after installation is essential. For instance, listen for unusual sounds or monitor fluid flow. These steps might seem minor, yet they significantly impact the solenoid valve's efficiency. Take the time to reflect on these aspects for better outcomes.
2026 How to Choose the Right Solenoid Valve for Your Application? - Key Specifications to Consider When Selecting a Solenoid Valve
| Specification | Description | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | The voltage required to operate the solenoid valve | 12V DC, 24V AC, 120V AC |
| Flow Rate | The volume of fluid that can pass through the valve per unit time | 0.5 - 50 GPM |
| Pressure Rating | Maximum pressure the valve can handle | 0 - 150 PSI |
| Body Material | Material from which the valve body is made | Brass, Stainless Steel, Plastic |
| Size | Diameter of the valve inlet and outlet | 1/4", 1/2", 1" |
| Actuation Type | Method used to open and close the valve | Direct-acting, Pilot-operated |
| Temperature Range | The range of temperatures the valve can operate under | -40°F to 190°F |
Evaluating Different Types of Solenoid Valves for Your Application
When selecting a solenoid valve, it's crucial to evaluate various types based on your specific needs. Solenoid valves come in several configurations. These include direct-acting, pilot-operated, and two-way or three-way designs. Each type has distinct features that cater to different applications. For example, direct-acting valves are ideal for low-pressure systems. However, they may not handle higher flow rates effectively.
Consider the medium you are working with. Some valves suit water or air, while others handle corrosive or high-temperature liquids. Material compatibility is vital. A mismatched valve can cause leaks or failures. Think about installation space too. Bulky valves might not fit in tight spots.
You should also reflect on operation frequency and duty cycle. Continuous use demands robust components. In contrast, intermittent use can tolerate lighter materials. Here’s a thought: overlooking these details could lead to performance issues. Evaluate your requirements thoroughly. Valid concerns about efficiency and durability should guide your choice.
2026 Solenoid Valve Type Comparison
Industry Standards and Certifications Affecting Solenoid Valve Selection
When selecting a solenoid valve, industry standards and certifications play a crucial role. Different sectors, such as automotive and oil and gas, have unique requirements. For instance, valves used in the oil industry must meet API standards. This ensures they can handle high pressures and corrosive environments effectively. A recent report from the International Society of Automation noted that compliance with specific standards boosts reliability in critical applications.
Additionally, certifications like ISO 9001 can significantly affect the selection process. These certifications indicate quality management systems are in place. A survey indicated that 70% of engineers prioritize certified products due to enhanced performance attributes. However, not all manufacturers invest in obtaining these certifications. This can lead to variances in quality and performance, creating potential risks.
Understanding the specific standards relevant to your application is imperative. Each industry’s operational environment dictates valve requirements. Ignoring these could lead to failures. Companies often overlook this, seeking cost savings instead. In reality, investing in certified valves can prevent costly downtime and enhance safety. The complexity of these standards is a challenge for many, demanding careful consideration and expert guidance.
Common Applications and Their Specific Solenoid Valve Requirements

When selecting the right solenoid valve, understanding the application is crucial. Different applications demand specific features. For instance, in water control systems, valves must resist corrosion. In machinery, valves require quick response times and durability. Each application shapes the type of solenoid valve needed.
Consider pneumatic systems. They often use solenoid valves that can handle high pressures. These valves should also permit rapid cycling. On the other hand, in HVAC systems, energy efficiency is key. Valves must maintain precise temperature control. Make sure to assess the surrounding environment. It may affect your valve's performance and lifespan.
Tips: Always check the voltage requirements before making a purchase. Verify compatibility with your system. Take time to research materials used in the valve. Corrosion-resistant options are often more reliable in tough environments. Don't overlook the need for periodic maintenance. This ensures longevity and better performance over time.
Related Posts
-
Unlocking the Efficiency of Cryogenic Solenoid Valves: A Deep Dive into Their Applications and Performance Data
-
Top 5 Benefits of Using Stainless Steel Solenoid Valves in Industry
-

Top Tips for Choosing and Maintaining Stainless Steel Solenoid Valves
-

2026 Best Stainless Steel Solenoid Valve Options for Your Needs?
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Right Check Valve for Your Project
-

The Essential Role of Cryogenic Valves in Modern Cryogenic Systems and Their Impact on Energy Efficiency
